The invention of the clock cannot be attributed to a single individual, as it is the culmination of centuries of advancements in timekeeping technology. The earliest mechanical clocks, which represented a significant leap in timekeeping, appeared in Europe during the late 13th and early 14th centuries. The exact inventor is unknown, but these early mechanical clocks set the stage for the modern clock.
In the 14th century, European clockmakers, working in monasteries and universities, began creating the first mechanical clocks. These were not portable timepieces but large installations in public places, like town squares and cathedrals. They were designed not only for timekeeping but also as symbols of communal pride and technological prowess
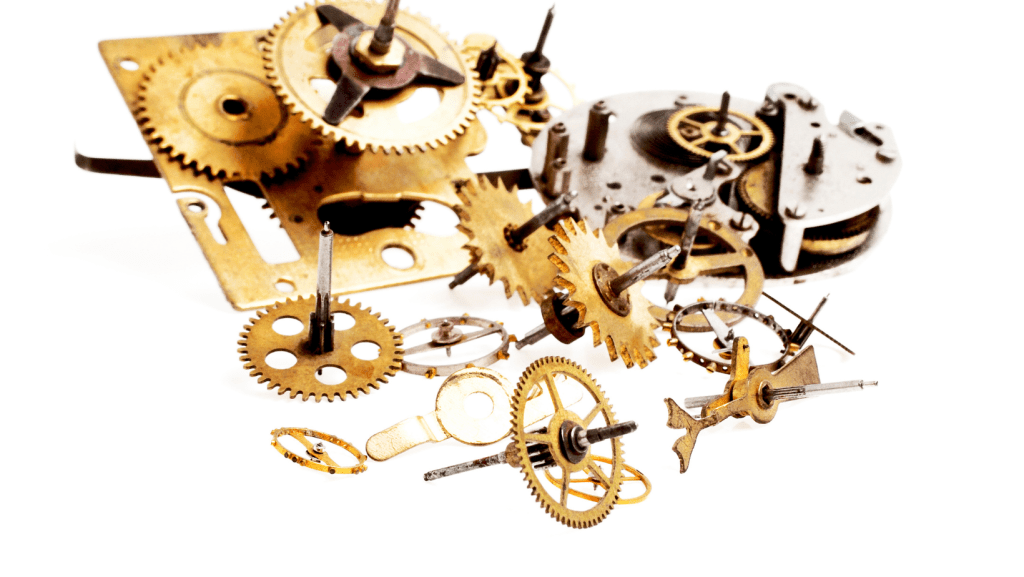
These early mechanical clocks were vastly different from their predecessors. They used an escapement mechanism, a technology that controls the unwinding of the clock’s driving force, to regulate the movement of the gear system. This innovation was key to transforming timekeeping from an approximation to a precise science.
In 1283, a reference to a mechanical clock in a church in Dunstable, England, marks one of the earliest known mentions of such a device. However, the identity of its creator remains shrouded in mystery. Similarly, the Salisbury Cathedral clock, dating back to 1386, is one of the oldest surviving examples of a mechanical clock, yet the records do not reveal the name of its maker.
As the technology spread across Europe, several clockmakers made significant contributions, each adding to the evolution of the clock. By the end of the 14th century, mechanical clocks were becoming more common in public spaces across Europe, indicating a growing expertise and interest in mechanical timekeeping.
The transition from these early mechanical clocks to smaller, more precise timepieces was gradual and involved numerous inventors and innovations. Therefore, the invention of the clock is a story of collective ingenuity and progress, rather than the achievement of a single inventor.
Credited to:https://historycooperative.org/